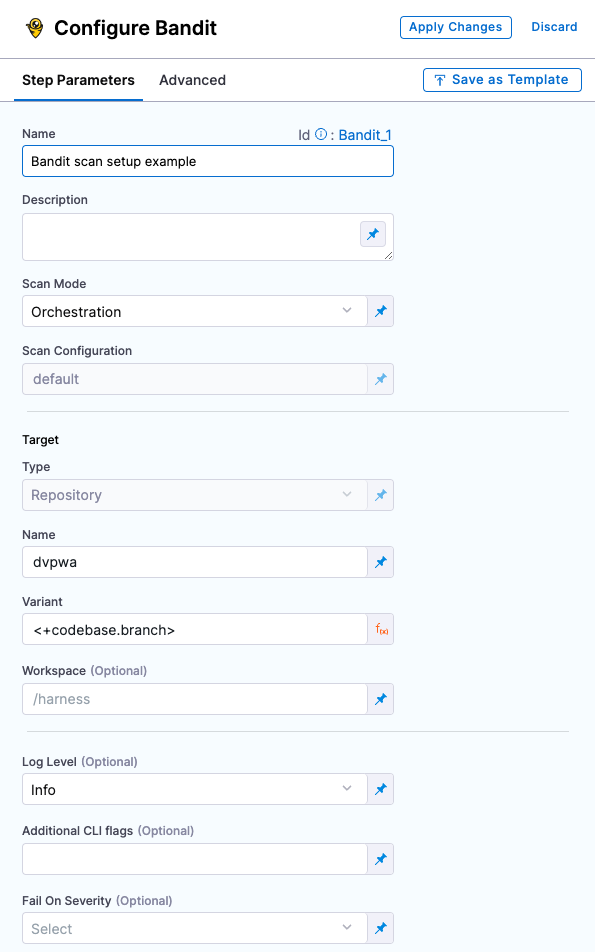
STO external scanner support and requirements
This section describes how to set up each of the external scanners supported by Harness STO.
For more information about STO support, go to What's supported in STO.
Scanner categories supported by STO
The following list shows the scan types that STO supports:
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing) scans a code repository and identifies known vulnerabilities in open-source and proprietary code.
- SCA (Software Composition Analysis) scans a code repository and identifies known vulnerabilities in open-source libraries and packages used by the code.
- Secret Scanning scans a code repository and identifies all secrets such as access keys and passwords.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) scans a running application for vulnerabilties by simulating a malicious external actor exploiting known vulnerabilties.
- Container Scanning identifies vulnerabilities in container images.
Data ingestion methods supported by STO
Harness Security Testing Orchestration integrates with multiple scanners and targets. Different types of scan approaches can be done on each scanner-target combination:
- Orchestration (
orchestratedScan) Scans are fully orchestrated. A Security step in the Harness pipeline orchestrates a scan and then normalizes and compresses the results. - Extraction (
dataLoad) Scans are partially orchestrated. The Security step pulls scan results from an external SaaS service and then normalizes and compresses the data. - Ingestion (
ingestionOnly) Scans are not orchestrated. The Security step ingests results from a previous scan (for a scan run in a previous step), and then normalizes and compresses the results.
The scanner, targets, and scan approach combinations are covered in the next section.
Scanners supported by STO
If you use a scanner that isn't listed in the following table, you can still ingest your scan results into STO.
-
If your scanner can publish to SARIF format, go to Ingest SARIF scan results into STO.
-
For other scanners, go to Ingest results from unsupported scanners.
| Scan Mode | Open Source | Commercial |
|---|---|---|
| SAST |
|
|
| SCA |
|
|
| Secrets |
|
|
| DAST |
| |
| Container Images |
|
|
| Configurations |
|
|
Scanner binaries used in STO container images
Harness maintains and updates a container image for every scanner supported by STO. The following table lists the binaries and versions used for the most popular scanners.
| Scanner | Binary | Current version |
|---|---|---|
| Aqua Trivy | trivy image | Latest stable build |
| Bandit | bandit | 1.7.4 |
| Black Duck Hub | synopsys detect | 9.0.0 |
| Brakeman | brakeman | 4.4.0 |
| Checkmarx | runCxConsole.sh | 1.1.26 |
| Grype | grype | Latest stable build |
| Nikto | Nikto | 2.1.6 |
| Nmap | nmap | 7.92 |
| Prowler | prowler | Latest stable build |
| SonarQube | sonar-scanner | 4.7.0.2747 |
| Twistlock | twistcli | 30.01.152 |
| Whitesource | java -jar /opt/whitesource/wss-unified-agent.jar | 23.5.2.1 |
Ingestion formats supported by STO
Harness STO can automatically ingest, aggregate, normalize, and deduplicate data from the following scanners and formats.
- Anchore Enterprise — JSON
- Aqua Security — JSON
- Aqua Trivy — JSON
- AWS ECR — JSON
- AWS Security Hub — JSON
- Bandit — JSON
- Black Duck Hub — JSON
- Brakeman — JSON
- Burp — XML
- Checkmarx — XML, SARIF
- CodeQL — JSON, SARIF
- Coverity — XML
- Data Theorem — JSON
- Docker Content Trust — JSON
- Fortify — JSON
- Fortify on Demand — JSON
- Fossa — JSON
- Gitleaks — JSON, SARIF
- HQL AppScan — XML
- Grype — JSON
- Mend (formerly Whitesource) — JSON
- Nessus — XML
- Nexus — JSON
- Nikto — XML
- Nmap — XML
- OpenVAS — JSON
- OWASP Dependency Check — JSON
- Prisma Cloud — JSON
- Prowler — JSON
- Qualys — XML
- Qwiet — JSON
- Reapsaw — JSON
- Semgrep — SARIF
- Snyk — JSON, SARIF
- SonarQube — JSON
- Sysdig — JSON
- Tenable — JSON
- Veracode — XML
- JFrog Xray — JSON
- Wiz - JSON (recommended), SARIF
- Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) — JSON
Operating systems and architectures supported by STO
STO uses CI build infrastructures to orchestrate scans and ingest issues. The following table shows STO support for each infrastructure type.
| Operating System | Architecture | Harness Cloud | Self-managed local runner | Self-managed AWS/GCP/Azure VMs | Self-managed Kubernetes cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linux | amd64 | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported |
| Linux | arm64 | ✅ Ingestion mode only | ✅ Ingestion mode only | ✅ Ingestion mode only | ✅ Ingestion mode only |
| Windows | amd64 | ✅ Ingestion mode only | ❌ Not supported | Roadmap | ❌ Not supported |
| MacOS | arm64 | Roadmap | Roadmap | Roadmap | ❌ Not supported |
Docker-in-Docker requirements for STO
The following use cases require a Docker-in-Docker background step in your pipeline:
- Container image scans on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for Orchestration and Dataload scan modes
- Security steps (not step palettes) on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for all target types and Orchestration/DataLoad modes
The following use cases do not require Docker-in-Docker:
- Harness Cloud AMD64 build infrastructures
- SAST/DAST/configuration scans that use scanner templates (not Security steps)
- Ingestion scans where the data file has already been generated
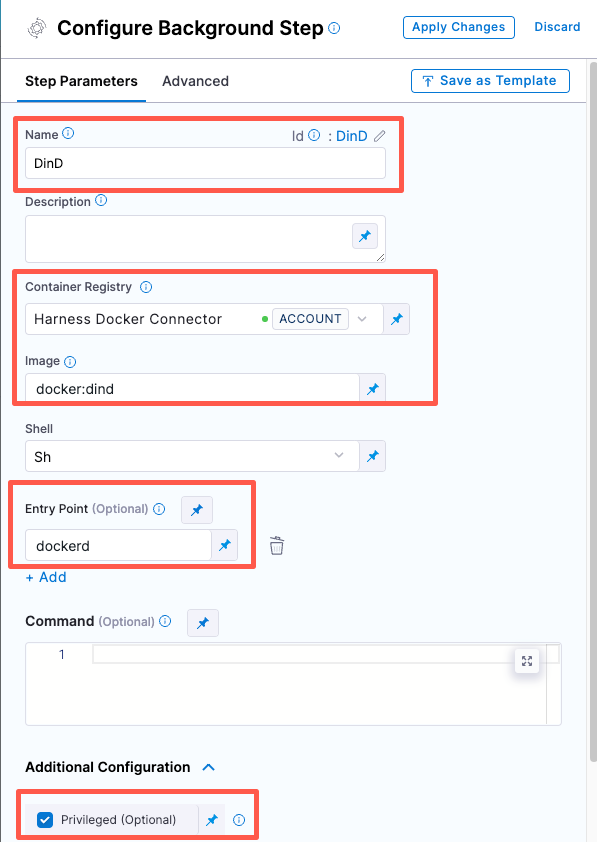
Set up a Docker-in-Docker background step
-
Go to the stage where you want to run the scan.
-
In Overview, add the shared path
/var/run. -
In Execution, do the following:
-
Click Add Step and then choose Background.
-
Configure the Background step as follows:
-
Dependency Name =
dind -
Container Registry = The Docker connector to download the DinD image. If you don't have one defined, go to Docker connector settings reference.
-
Image =
docker:dind -
Under Entry Point, add the following:
dockerdIn most cases, using
dockerdis a faster and more secure way to set up the background step. For more information, go to the TLS section in the Docker quick reference.
If the DinD service doesn't start with
dockerd, clear the Entry Point field and then run the pipeline again. This starts the service with the default entry point.- Under Optional Configuration, select the Privileged checkbox.
-
-
- Visual setup
- YAML setup
Add a Background step to your pipeline and set it up as follows:
- step:
type: Background
name: background-dind-service
identifier: Background_1
spec:
connectorRef: CONTAINER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker:dind
shell: Sh
entrypoint:
- dockerd
privileged: true
Root access requirements for STO
You need to run the scan step with root access if either of the following apply:
-
You need to run a Docker-in-Docker background service.
-
You need to add trusted certificates to your scan images at runtime.
You can set up your STO scan images and pipelines to run scans as non-root and establish trust for your own proxies using custom certificates. For more information, go to Configure STO to Download Images from a Private Registry.
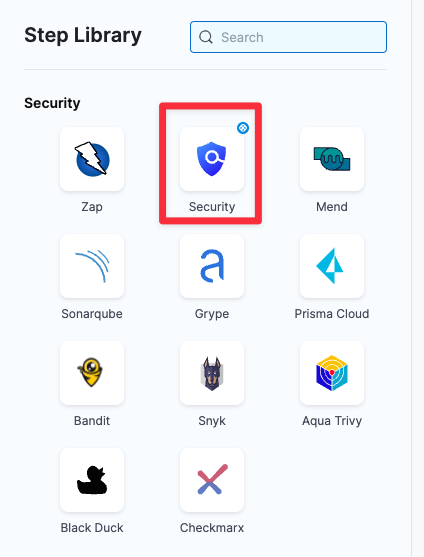
Security steps and scanner templates in STO
The Step library includes a Security step for setting up scanners: open the step and configure the scan as a set of key/value pairs under Settings.
Some scanners also have scanner templates with UIs that simplify the process of setting up a scanner.
Step Library with Security step and scanner templates
Security step configuration
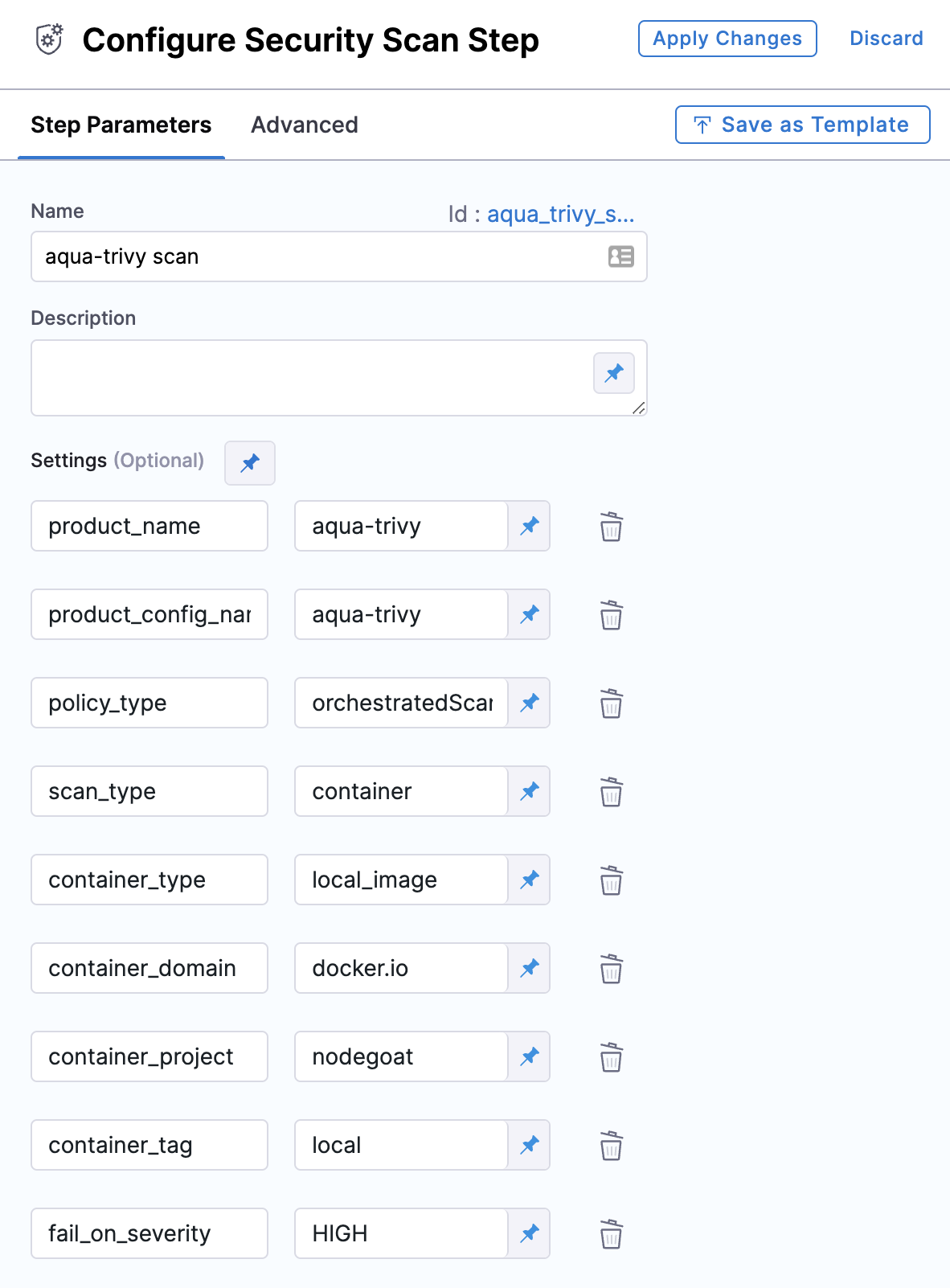
Scanner template configuration